If your sales conversations often end without a clear next step, you need a sales sequence.
A sales sequence is a series of steps that move a prospect from initial contact to a closed sale. It’s a roadmap that helps you build trust, establish credibility, and persuade the prospect to take action. Without a clear sales sequence, you’ll find yourself waving at opportunities as they slip through the cracks.
In this article, we’ll explore the key components of a successful sales sequence and provide practical tips for developing your own. Whether you’re a seasoned sales professional or a novice, a well-designed sales sequence can help you streamline your sales process and close more deals.
Let’s dive in!
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Sales Sequences
A sales sequence typically consists of several stages, including the following:
- Prospecting – Identifying potential customers and reaching out to them to introduce your product or service.
- Qualifying – Determining if the customer is a good fit for your product or service and if they have the budget and authority to make a purchase.
- Presenting – Demonstrating the features and benefits of your product or service and addressing any objections or concerns the customer may have.
- Closing – Asking for the sale, negotiating, and overcoming any final objections.
- Following up – Staying in touch with the customer after the sale to make sure they’re happy and identify any additional needs.
While these steps will naturally unfold as part of a successful purchase, it’s crucial not to leave things to chance. There will be times when deals get stuck, prospects aren’t sure what to do next, and unless you have a structured process, the deal will be lost.
The goal is to have a series of SOP-like steps you can follow to progress the deals from new to closed-won.
Types of Sales Sequences
There are several types of sales sequences, including linear, branching, and parallel.
A linear sales sequence involves following a set path from prospecting to closing. The process typically begins with prospecting, where sales reps identify potential leads. They make initial contact and qualify these leads. Following qualification, the sales rep presents the offer to the prospect, addressing objections and offering tailored solutions. Finally, they close the deal by presenting a proposal that aligns with the prospect’s needs and budget.
The linear sales sequence is straightforward and structured, offering predictability for both sales representatives and prospects. It’s easy to implement and manage, too. However, it’s quite rigid, which may make it less effective when accommodating customers’ different needs and preferences.
A branching sales sequence, on the other hand, adapts the sequence based on the customer’s needs and interests. It starts similarly with prospecting and initial contact, but instead of following a fixed sequence, the sales rep dynamically adjusts their approach based on the customer’s responses and preferences.
For example, you might offer multiple presentations if the purchase involves a buying committee with different stakeholders.

Unlike the linear sales sequence, the branching sales sequence enhances engagement by providing a more personalized sales experience. Sales representatives can respond dynamically to objections and concerns, fostering deeper connections with prospects. However, managing a branching sequence requires more effort and resources, and complexity can increase as the number of branching options grows.
Finally, a parallel sales sequence involves running multiple sequences simultaneously for different products or services.
It offers flexibility to different customer personas. However, coordinating parallel sequences is a challenge. Complexity escalates with the number of sequences; the potential overlap among sales teams working on different sequences requires a clear delineation of responsibilities to avoid conflicts.
Ultimately, each type of sales sequence has its own advantages and disadvantages. The best approach will depend on your product and your customers’ preferences.
Creating Effective Sales Sequences
Step 1. Identifying Target Audience
Before you start creating your sales sequence, it’s important to understand your target audience deeply. What are their pain points? What motivates them to make a purchase? Once you answer these questions, you can tailor your messaging and sales approach to resonate with your audience.
Step 2. Crafting Compelling Messaging
When it comes to sales sequences, less is often more. Keep your messaging simple and to the point, focusing on the benefits of your product or service. Avoid overwhelming your leads with too much information or too many options, as this can lead to decision paralysis.
Use your lead’s name and other relevant information you have about them to create a more personalized experience.
Step 3. Setting Timing and Frequency
Make sure that you are reaching out to potential customers at the right time and with the right frequency. Research your customer’s buying journey and tailor your sales sequence to match.
Don’t forget to follow up! 80% of successful sales require at least five follow-ups, so don’t get discouraged. Instead, share case studies, social proof, and other materials addressing your customers’ concerns and heightening the need for your solution.
Step 4. Implementing Sales Sequences in Salesforce
Since Match My Email syncs emails to Salesforce, we’ll show you how to implement sales sequences in this CRM. However, you should have no issues implementing them in other CRMs.
4.1. Implementing Linear Sales Sequences in Salesforce
You’ll need the following features to implement linear sales sequences in Salesforce:
- Lead and Opportunity Management: Use Salesforce’s lead and opportunity management features to track prospects as they move through the sales process.
- Workflow Automation: Create workflows to automate repetitive tasks and standardize the sales process. Define specific actions and criteria that will trigger workflow rules as prospects progress through different stages.
- Sales Path: Configure Sales Path to provide a visual representation of the linear sales process, showing sales reps what to do next.
4.2. Salesforce Features You Need to Implement Branching Sales Sequences
If you want to customize your approach based on customers’ needs, use the following Salesforce features:
- Custom Fields and Objects: Customize Salesforce by creating custom fields and objects to capture additional information about prospects and their preferences.
- Process Builder and Flows: Use Process Builder and Flow Builder to create dynamic processes that branch based on specific criteria or conditions. Define decision points where the sequence can adapt based on prospect responses or actions.
- Dynamic Page Layouts: Configure dynamic page layouts to display relevant information and fields based on the prospect’s characteristics or stages in the sales process.

4.3. How to Set up Parallel Sales Sequences
Finally, parallel sales sequences require a more robust setup. Work with experts to reduce complexity and conflicts.
- Multiple Sales Processes: Set up multiple sales processes within Salesforce to manage parallel sequences for different products or services. Define separate stages, milestones, and actions for each.
- Territory Management: Utilize Salesforce’s Territory Management feature to assign leads and opportunities to different sales teams or territories based on product specialization or geographic regions.
- Campaign Management: Implement Salesforce’s Campaign Management functionality to track and manage marketing campaigns associated with each product or service. Link campaigns to specific sales processes to align marketing with sales.
Bonus: Ensure You Have the Right Integrations
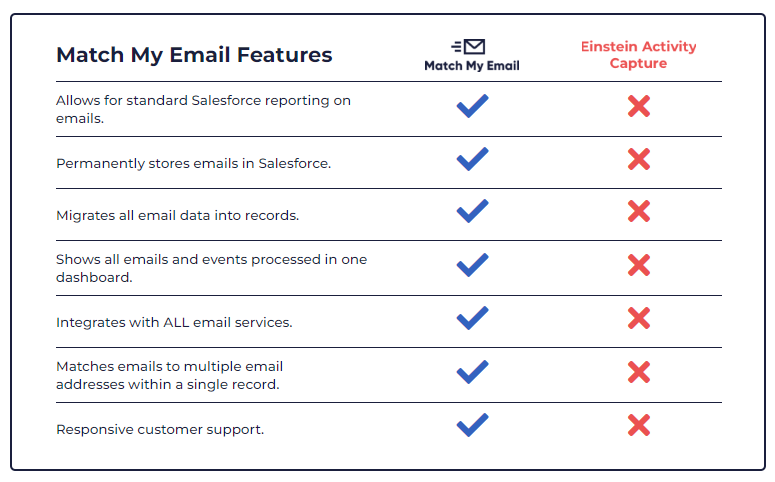
If your team uses Gmail or Outlook to communicate with prospects, you probably know how clunky Salesforce’s integrations can be. Einstein Activity Capture doesn’t permanently store data, so you won’t be able to report on the emails and events, creating a huge gap where there should be information pointing you to bottlenecks.
Fortunately, Match My Email offers automatic email and calendar sync with Salesforce. You’ll get permanent data storage, allowing you to build Flows and reports based on your correspondence data.
Plus, you’ll be able to see the relevant information in your central HQ: your CRM.
We built Match My Email to make your work easier. We’re a long-standing ISV partner with Salesforce and our average AppExchange rating is 4.94/5.
Measuring Success
Once you’ve implemented your sales sequence, it’s time to improve.
Firstly, identify the relevant key performance indicators (KPIs). These may include conversion rates, average order value, and customer lifetime value.
Then, regularly analyze your data and perform the necessary optimizations. This may involve A/B testing different messaging or offers, adjusting your targeting criteria, or optimizing your follow-up sequence.
If you can’t see it, you can’t improve it. Proper analysis allows you to spot the gaps and fill them with powerful processes!
Take It Step by Step
These sequences aren’t just about following steps. They’re about understanding and adapting to customers’ needs and behaviors.
Whether guiding a prospect through a linear path, tailoring the journey based on branching decisions, or efficiently managing multiple sales processes in parallel, each approach offers distinct advantages for engaging prospects.
Once you implement your sequences within Salesforce, you’ll get a structured framework you can follow to exceed this quarter’s quotas.
At the end of the day, mastering sequences isn’t just a sales strategy. It’s the secret sauce to unlocking greater conversions, happier customers, and unstoppable growth.